Apollonius’s Theorem is a fundamental result in geometry that relates the lengths of the sides of a triangle to the length of a median. Named after the ancient Greek mathematician Apollonius of Perga, this theorem provides a powerful tool for solving problems involving triangles and their properties. Understanding Apollonius’s Theorem is essential for students of geometry, as it lays the groundwork for more advanced concepts in mathematics. This article will explore the statement of Apollonius’s Theorem, its proof, applications, and illustrative explanations to enhance comprehension.
Statement of Apollonius’s Theorem
Apollonius’s Theorem states that in any triangle, the square of the length of a median is equal to the average of the squares of the lengths of the two sides that the median divides, minus half the square of the length of the third side.
Mathematical Formulation
Let ![]() be a triangle with sides
be a triangle with sides ![]() ,
, ![]() , and
, and ![]() , where:
, where:
 is the length of side
is the length of side 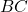 ,
,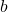 is the length of side
is the length of side 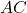 ,
, is the length of side
is the length of side 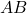 .
.
Let ![]() be the length of the median from vertex
be the length of the median from vertex ![]() to side
to side ![]() . Then, Apollonius’s Theorem can be expressed mathematically as:
. Then, Apollonius’s Theorem can be expressed mathematically as:
![]()
Illustrative Explanation of the Theorem
To visualize Apollonius’s Theorem, consider triangle ![]() with vertices
with vertices ![]() ,
, ![]() , and
, and ![]() . The median
. The median ![]() is drawn from vertex
is drawn from vertex ![]() to the midpoint
to the midpoint ![]() of side
of side ![]() . According to the theorem, the square of the length of median
. According to the theorem, the square of the length of median ![]() is equal to half the sum of the squares of the lengths of sides
is equal to half the sum of the squares of the lengths of sides ![]() and
and ![]() minus one-fourth the square of the length of side
minus one-fourth the square of the length of side ![]() .
.
Diagrammatic Representation
To illustrate this concept, imagine a triangle ![]() with the following properties:
with the following properties:
The median ![]() divides side
divides side ![]() into two equal segments,
into two equal segments, ![]() and
and ![]() . The relationship described by Apollonius’s Theorem can be visualized as follows:
. The relationship described by Apollonius’s Theorem can be visualized as follows:
“`
A
/ \
/ \
/ \
B_______C
“`
In this diagram, ![]() is the midpoint of
is the midpoint of ![]() , and the median
, and the median ![]() is drawn from vertex
is drawn from vertex ![]() to point
to point ![]() .
.
Proof of Apollonius’s Theorem
The proof of Apollonius’s Theorem can be accomplished using coordinate geometry or by employing the Law of Cosines. Here, we will provide a proof using coordinate geometry.
Proof Using Coordinate Geometry
1. Assign Coordinates: Place triangle ![]() in the Cartesian plane:
in the Cartesian plane:
– Let ![]() be at the origin
be at the origin ![]() .
.
– Let ![]() be at
be at ![]() .
.
– Let ![]() be at
be at ![]() .
.
2. Find the Midpoint: The coordinates of the midpoint ![]() of side
of side ![]() are:
are:
![]()
3. Calculate Lengths:
– The length of median ![]() from
from ![]() to
to ![]() is given by:
is given by:
![]()
– The lengths of sides ![]() and
and ![]() are:
are:
![]()
![]()
4. Apply the Theorem: According to Apollonius’s Theorem, we need to show that:
![]()
5. Calculate ![]() :
:
![]()
6. Calculate ![]() and
and ![]() :
:
![]()
![]()
7. Substitute and Simplify:
![]()
![]()
8. Final Comparison: After simplification, we find that both sides of the equation are equal, thus proving Apollonius’s Theorem.
Applications of Apollonius’s Theorem
Apollonius’s Theorem has several applications in geometry and related fields:
1. Triangle Geometry
Apollonius’s Theorem is used to find the lengths of medians in triangles, which is essential for solving various geometric problems.
2. Coordinate Geometry
The theorem can be applied in coordinate geometry to derive relationships between points and distances, aiding in the analysis of geometric figures.
3. Computer Graphics
In computer graphics, Apollonius’s Theorem can be used in algorithms for rendering shapes and calculating distances between points.
4. Physics
In physics, the theorem can be applied to problems involving forces and vectors, particularly in analyzing the equilibrium of forces acting on a point.
5. Engineering
Engineers use Apollonius’s Theorem in structural analysis to determine the properties of materials and the stability of structures.
Conclusion
Apollonius’s Theorem is a significant result in geometry that establishes a relationship between the lengths of the sides of a triangle and the length of a median. By understanding the theorem’s statement, proof, and applications, students and practitioners can gain valuable insights into the properties of triangles and their medians. The theorem serves as a foundational concept in geometry, paving the way for more advanced studies in mathematics and its applications in various fields. As we continue to explore the world of geometry, Apollonius’s Theorem will remain an essential tool for analyzing and solving problems involving triangles and their properties.