Ethanoic acid, commonly known as acetic acid, is a colorless liquid organic compound with a pungent smell and a sour taste. It is one of the simplest carboxylic acids and is widely used in various industries, including food, pharmaceuticals, and chemical manufacturing. This article will provide an exhaustive exploration of ethanoic acid, covering its chemical structure, properties, production methods, applications, and significance in different contexts.
Chemical Structure and Properties
1. Chemical Formula: Ethanoic acid is represented by the chemical formula ![]() or
or ![]() . The structure consists of a methyl group (
. The structure consists of a methyl group (![]() ) attached to a carboxyl group (
) attached to a carboxyl group (![]() ), which is characteristic of carboxylic acids.
), which is characteristic of carboxylic acids.
2. Molecular Structure: The molecular structure of ethanoic acid can be depicted as follows:
![]()
In this structure, the carbon atom in the carboxyl group is double-bonded to one oxygen atom and single-bonded to a hydroxyl group (![]() ). The other carbon atom is bonded to three hydrogen atoms.
). The other carbon atom is bonded to three hydrogen atoms.
3. Physical Properties:
- Appearance: Ethanoic acid is a colorless liquid.
- Odor: It has a strong, pungent odor that is often associated with vinegar.
- Taste: Ethanoic acid has a sour taste, which is why it is commonly found in vinegar.
- Boiling Point: The boiling point of ethanoic acid is approximately 118 °C (244 °F).
- Melting Point: Its melting point is around 16.6 °C (61.88 °F), which means it can exist as a solid at lower temperatures.
- Solubility: Ethanoic acid is highly soluble in water due to its ability to form hydrogen bonds with water molecules. It is also soluble in organic solvents such as ethanol and ether.
4. Chemical Properties:
- Acidity: Ethanoic acid is a weak acid, meaning it partially dissociates in water to release hydrogen ions (
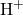 ):
):
![]()
The equilibrium indicates that not all molecules of ethanoic acid dissociate, which is characteristic of weak acids.
- Reactivity: Ethanoic acid can react with bases to form salts and water in a neutralization reaction. It can also undergo esterification reactions with alcohols to form esters, which are important in the production of fragrances and flavorings.
Production of Ethanoic Acid
Ethanoic acid can be produced through several methods, including:
1. Fermentation: One of the oldest methods of producing ethanoic acid is through the fermentation of carbohydrates. This process involves the conversion of sugars (such as glucose) into ethanol by yeast, followed by the oxidation of ethanol to acetic acid by acetic acid bacteria (e.g., Acetobacter species). This method is commonly used in the production of vinegar, which typically contains 4-8% acetic acid.
2. Synthetic Methods:
- Carbonylation of Methanol: A modern industrial method involves the carbonylation of methanol, where methanol reacts with carbon monoxide in the presence of a catalyst (such as rhodium or iridium) to produce ethanoic acid:
![]()
- Oxidation of Ethanol: Ethanol can also be oxidized to produce ethanoic acid. This can be achieved using various oxidizing agents, such as potassium permanganate or chromium trioxide.
3. Hydrolysis of Acetyl Chloride: Ethanoic acid can be produced by the hydrolysis of acetyl chloride (![]() ) in the presence of water:
) in the presence of water:
![]()
Applications of Ethanoic Acid
Ethanoic acid has a wide range of applications across various industries:
1. Food Industry: Ethanoic acid is commonly used as a food preservative and flavoring agent. It is the main component of vinegar, which is used in cooking, pickling, and as a condiment. The acidity of vinegar helps inhibit the growth of bacteria and molds, making it an effective preservative.
2. Chemical Industry: Ethanoic acid is a key raw material in the production of various chemicals, including:
- Esters: Ethanoic acid is used to produce esters, which are important in the manufacture of fragrances, flavorings, and solvents.
- Acetic Anhydride: This compound is derived from ethanoic acid and is used in the production of cellulose acetate, which is used in photographic films and coatings.
- Sodium Acetate: Ethanoic acid is used to produce sodium acetate, which is used in food preservation and as a buffering agent in biochemical applications.
3. Pharmaceuticals: Ethanoic acid is used in the synthesis of various pharmaceutical compounds, including analgesics, anti-inflammatory drugs, and antibiotics. Its derivatives are also used in the formulation of medications.
4. Textile Industry: Ethanoic acid is used in the textile industry for dyeing and finishing processes. It helps in the fixation of dyes on fabrics and improves the quality of the final product.
5. Cleaning Products: Due to its acidic nature, ethanoic acid is used in various cleaning products. It can effectively remove mineral deposits, soap scum, and other residues, making it a popular ingredient in household cleaners.
6. Laboratory Reagent: Ethanoic acid is widely used in laboratories as a reagent for various chemical reactions, including titrations and synthesis of organic compounds.
Significance of Ethanoic Acid
Ethanoic acid is significant for several reasons:
1. Biological Importance: Ethanoic acid plays a role in various biological processes. It is involved in the metabolism of carbohydrates and fats, and it is a key component of the citric acid cycle, which is essential for energy production in living organisms.
2. Environmental Impact: Ethanoic acid is biodegradable and has a relatively low environmental impact compared to other organic solvents. Its use in food preservation and cleaning products can help reduce the reliance on synthetic chemicals that may be harmful to the environment.
3. Cultural Relevance: Ethanoic acid, particularly in the form of vinegar, has cultural significance in many cuisines around the world. It is used in traditional dishes, pickling processes, and as a condiment, reflecting its importance in culinary practices.
4. Economic Value: The production and use of ethanoic acid contribute significantly to the economy. It is a valuable commodity in various industries, and its versatility makes it an essential chemical in both industrial and consumer applications.
Conclusion
Ethanoic acid, or acetic acid, is a vital organic compound with a wide range of applications and significance in various fields. Its unique chemical structure, properties, and production methods make it an essential ingredient in food, pharmaceuticals, textiles, and cleaning products. Understanding ethanoic acid’s role in biological processes, environmental impact, and cultural relevance highlights its importance in our daily lives.
As we continue to explore the complexities of organic chemistry and its applications, ethanoic acid will remain a key focus of research and development, providing insights into its potential uses and benefits in various industries. Its versatility and significance underscore the importance of this simple yet powerful compound in both scientific and practical contexts.