Relative speed is a fundamental concept in physics and kinematics that describes the velocity of one object as observed from another object. It is particularly important in scenarios involving multiple moving objects, as it allows for a clearer understanding of their interactions and motions relative to one another. This comprehensive article will delve into the definition of relative speed, its mathematical formulation, applications, significance, and examples, providing a thorough overview of this essential topic.
Definition of Relative Speed
Relative speed refers to the speed of one object as observed from another object. It is the difference in velocities of two objects when they are moving in the same direction or the sum of their velocities when they are moving in opposite directions. Understanding relative speed is crucial for analyzing motion in various contexts, such as collisions, overtaking, and the movement of objects in different frames of reference.
Mathematical Formulation of Relative Speed
The mathematical formulation of relative speed depends on the direction of motion of the objects involved. The following equations summarize the key concepts:
1. Objects Moving in the Same Direction: When two objects are moving in the same direction, the relative speed (![]() ) of one object with respect to the other can be calculated as:
) of one object with respect to the other can be calculated as:
![]()
where:
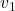 is the speed of the first object,
is the speed of the first object,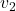 is the speed of the second object.
is the speed of the second object.
In this case, if ![]() is greater than
is greater than ![]() , the relative speed will be positive, indicating that the first object is moving faster than the second.
, the relative speed will be positive, indicating that the first object is moving faster than the second.
2. Objects Moving in Opposite Directions: When two objects are moving in opposite directions, the relative speed is the sum of their speeds:
![]()
This equation indicates that the distance between the two objects is decreasing at a rate equal to the sum of their speeds.
Examples of Relative Speed
To illustrate the concept of relative speed, consider the following examples:
1. Example 1: Two Cars on a Highway: Suppose Car A is traveling at a speed of 80 km/h, and Car B is traveling at a speed of 60 km/h in the same direction. The relative speed of Car A with respect to Car B can be calculated as:
![]()
This means that Car A is moving 20 km/h faster than Car B.
2. Example 2: Two Trains Approaching Each Other: Consider Train X moving at 90 km/h and Train Y moving at 70 km/h in opposite directions. The relative speed of Train X with respect to Train Y is:
![]()
This indicates that the distance between the two trains is closing at a rate of 160 km/h.
3. Example 3: A Boat in a River: Imagine a boat moving upstream at 10 km/h relative to the water and the river current flowing downstream at 5 km/h. The effective speed of the boat relative to the riverbank can be calculated as:
![]()
This means the boat is effectively moving upstream at 5 km/h relative to the riverbank.
Applications of Relative Speed
Relative speed has numerous applications across various fields, including:
1. Collision Analysis: In accident reconstruction, understanding the relative speeds of vehicles involved in a collision is crucial for determining the dynamics of the crash and assessing liability.
2. Sports: In sports such as racing, understanding the relative speed of competitors can provide insights into strategies for overtaking and positioning.
3. Aerospace: In aviation and space exploration, relative speed is essential for calculating the approach and separation of aircraft and spacecraft, particularly during docking maneuvers.
4. Navigation: Relative speed is important in navigation systems, where the speed of a vessel or aircraft must be considered in relation to the speed of the surrounding environment, such as currents or winds.
5. Physics and Engineering: In physics, relative speed is used to analyze motion in different frames of reference, while in engineering, it is crucial for designing systems that involve moving parts, such as gears and conveyor belts.
Significance of Relative Speed
The significance of relative speed extends beyond its applications:
1. Fundamental Understanding of Motion: Relative speed is a key concept in kinematics, providing insights into how objects interact and move in relation to one another. It helps in understanding the principles of motion and the effects of different velocities.
2. Frame of Reference: The concept of relative speed emphasizes the importance of the observer’s frame of reference in analyzing motion. Different observers may perceive the same motion differently based on their own velocities.
3. Problem Solving: Understanding relative speed is essential for solving various physics problems, particularly those involving multiple moving objects. It allows for the application of mathematical principles to real-world scenarios.
4. Educational Value: Relative speed is a common topic in physics education, helping students grasp fundamental concepts related to motion, velocity, and acceleration. It serves as a practical example for applying mathematical principles to real-world situations.
Conclusion
In conclusion, relative speed is a fundamental concept in physics that describes the velocity of one object as observed from another object. It is determined by the difference in velocities of two objects moving in the same direction or the sum of their velocities when moving in opposite directions. Understanding relative speed enhances our knowledge of motion and its interactions, providing valuable insights into various applications across multiple fields. As research continues to advance, the study of relative speed will remain a dynamic area of exploration, driving innovations that contribute to our understanding of physical phenomena and the development of new technologies. The future of research related to relative speed holds great promise, with ongoing developments aimed at harnessing its principles for improving navigation systems, enhancing safety in transportation, and advancing scientific knowledge. By addressing the challenges posed by relative motion, we can enhance our ability to design and implement systems that meet the demands of modern society while promoting scientific advancement and environmental stewardship.