Algebraic expressions are fundamental components of algebra, a branch of mathematics that deals with symbols and the rules for manipulating those symbols. An algebraic expression is a combination of numbers, variables, and operations that represent a mathematical relationship. Understanding algebraic expressions is crucial for solving equations, modeling real-world situations, and advancing in mathematics. This article will explore the definition of algebraic expressions, their components, types, operations, and illustrative explanations to enhance comprehension.
What is an Algebraic Expression?
Definition of an Algebraic Expression
An algebraic expression is a mathematical phrase that can include numbers, variables (letters that represent unknown values), and operations such as addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division. Unlike equations, algebraic expressions do not contain an equality sign.
- Illustrative Explanation: Consider the expression
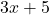 . This expression consists of the variable
. This expression consists of the variable 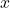 , the coefficient
, the coefficient 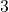 (which multiplies the variable), and the constant
(which multiplies the variable), and the constant 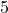 . It represents a quantity that depends on the value of
. It represents a quantity that depends on the value of 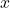 .
.
Components of Algebraic Expressions
Algebraic expressions are made up of several key components:
1. Variables: Symbols that represent unknown values. Common variables include ![]() ,
, ![]() , and
, and ![]() .
.
– Example: In the expression ![]() ,
, ![]() is the variable.
is the variable.
2. Coefficients: Numerical factors that multiply the variables. Coefficients can be positive or negative.
– Example: In the expression ![]() ,
, ![]() is the coefficient of the variable
is the coefficient of the variable ![]() .
.
3. Constants: Fixed values that do not change. Constants can be whole numbers, fractions, or decimals.
– Example: In the expression ![]() ,
, ![]() is the constant.
is the constant.
4. Operators: Symbols that represent mathematical operations, such as addition (+), subtraction (-), multiplication (×), and division (÷).
– Example: In the expression ![]() , the operator is subtraction.
, the operator is subtraction.
Illustrative Example of Components
Consider the expression ![]() :
:
- Variables:
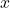 (appears in two terms)
(appears in two terms) - Coefficients:
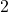 (for
(for 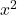 ),
), 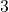 (for
(for 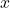 )
) - Constant:
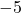
- Operators:
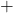 (addition),
(addition),  (subtraction)
(subtraction)
Types of Algebraic Expressions
Algebraic expressions can be classified into several types based on their structure and the number of terms they contain:
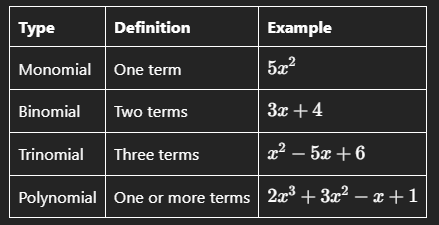
1. Monomial
A monomial is an algebraic expression that consists of a single term. It can be a constant, a variable, or a product of constants and variables.
- Example:
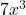 ,
, 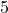 , and
, and 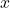 are all monomials.
are all monomials.
2. Binomial
A binomial is an algebraic expression that consists of two terms separated by a plus or minus sign.
- Example:
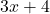 and
and 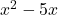 are binomials.
are binomials.
3. Trinomial
A trinomial is an algebraic expression that consists of three terms separated by plus or minus signs.
- Example:
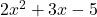 is a trinomial.
is a trinomial.
4. Polynomial
A polynomial is an algebraic expression that consists of one or more terms, where each term is a monomial. Polynomials can have any number of terms, including monomials, binomials, and trinomials.
- Example:
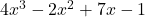 is a polynomial with four terms.
is a polynomial with four terms.
Illustrative Summary of Types
Operations on Algebraic Expressions
Algebraic expressions can be manipulated through various operations, including addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division. Understanding these operations is essential for simplifying expressions and solving equations.
1. Addition of Algebraic Expressions
To add algebraic expressions, combine like terms (terms that have the same variable raised to the same power).
- Example:
![]()
2. Subtraction of Algebraic Expressions
To subtract algebraic expressions, distribute the negative sign and then combine like terms.
- Example:
![]()
3. Multiplication of Algebraic Expressions
To multiply algebraic expressions, use the distributive property (also known as the FOIL method for binomials) and combine like terms.
- Example:
![]()
4. Division of Algebraic Expressions
To divide algebraic expressions, factor the numerator and denominator (if possible) and simplify.
- Example:
![]()
Illustrative Summary of Operations
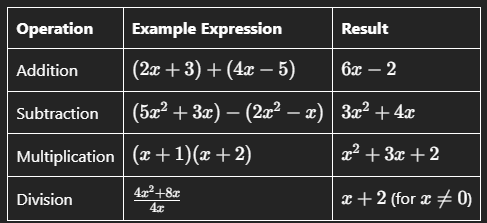
Applications of Algebraic Expressions
Algebraic expressions have numerous applications across various fields:
1. Mathematics
Algebraic expressions are foundational in algebra, calculus, and higher mathematics. They are used to formulate equations and inequalities.
2. Physics
In physics, algebraic expressions are used to represent relationships between physical quantities, such as distance, speed, and time.
3. Economics
Economists use algebraic expressions to model economic relationships, such as supply and demand, cost functions, and profit maximization.
4. Engineering
In engineering, algebraic expressions are used to design systems, analyze structures, and solve problems related to materials and forces.
5. Computer Science
In computer science, algebraic expressions are used in algorithms, programming, and data analysis to manipulate and process information.
Conclusion
Algebraic expressions are essential components of algebra that represent mathematical relationships using numbers, variables, and operations. Understanding the components, types, and operations of algebraic expressions is crucial for solving equations, modeling real-world situations, and advancing in mathematics. From basic arithmetic to complex problem-solving, algebraic expressions play a vital role in various fields, including mathematics, physics, economics, engineering, and computer science. As we continue to explore the world of mathematics, the study of algebraic expressions will remain a fundamental aspect of our analytical toolkit, enabling us to navigate the complexities of numerical relationships effectively.