A hollow cylinder, also known as a cylindrical shell, is a three-dimensional geometric shape that consists of two concentric circular bases connected by a curved surface. This shape is commonly encountered in various fields, including engineering, architecture, and manufacturing. Understanding the area of a hollow cylinder is essential for applications such as calculating material requirements, designing pipes, and analyzing structural components. This article aims to provide an exhaustive overview of the area of a hollow cylinder, detailing its definition, formulas, properties, and illustrative explanations for each concept.
1. Definition of a Hollow Cylinder
A hollow cylinder is defined as a cylindrical shape that has an inner radius (![]() ) and an outer radius (
) and an outer radius (![]() ). The height (
). The height (![]() ) of the cylinder is the perpendicular distance between the two circular bases. The hollow cylinder can be visualized as a tube or pipe, where the space between the inner and outer surfaces is empty.
) of the cylinder is the perpendicular distance between the two circular bases. The hollow cylinder can be visualized as a tube or pipe, where the space between the inner and outer surfaces is empty.
1.1. Components of a Hollow Cylinder
- Inner Radius (
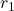 ): The radius of the inner circular base.
): The radius of the inner circular base. - Outer Radius (
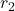 ): The radius of the outer circular base.
): The radius of the outer circular base. - Height (
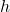 ): The distance between the two bases, measured along the axis of the cylinder.
): The distance between the two bases, measured along the axis of the cylinder.
2. Surface Area of a Hollow Cylinder
The surface area of a hollow cylinder consists of two main components: the lateral (curved) surface area and the area of the two circular bases. The total surface area can be calculated using the following formulas:
2.1. Lateral Surface Area
The lateral surface area of a hollow cylinder is the area of the curved surface that connects the two bases. It can be calculated using the formula:
![]()
- Illustrative Explanation: To visualize this, imagine unrolling the curved surface of the hollow cylinder into a rectangle. The height of the rectangle is
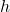 , and the width is the average circumference of the two bases, which is
, and the width is the average circumference of the two bases, which is 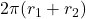 . Thus, the lateral surface area is the product of the height and the average circumference.
. Thus, the lateral surface area is the product of the height and the average circumference.
2.2. Area of the Circular Bases
The area of the circular bases can be calculated as follows:
![]()
This formula represents the area of the outer base minus the area of the inner base, effectively giving the area of the annular region formed by the two circles.
- Illustrative Explanation: If you think of the two bases as two circles, the area of the outer circle is
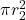 , and the area of the inner circle is
, and the area of the inner circle is 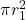 . The difference between these two areas gives the area of the annular region.
. The difference between these two areas gives the area of the annular region.
2.3. Total Surface Area
The total surface area of the hollow cylinder is the sum of the lateral surface area and the area of the circular bases:
![]()
Substituting the formulas, we get:
![]()
This can be simplified to:
![]()
3. Example Calculation
To illustrate the calculation of the area of a hollow cylinder, let’s consider an example:
Example:
Suppose we have a hollow cylinder with the following dimensions:
- Inner radius (
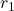 ) = 3 cm
) = 3 cm - Outer radius (
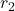 ) = 5 cm
) = 5 cm - Height (
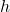 ) = 10 cm
) = 10 cm
Step 1: Calculate the Lateral Surface Area
Using the formula for lateral surface area:
![]()
Step 2: Calculate the Area of the Circular Bases
Using the formula for the area of the circular bases:
![]()
Step 3: Calculate the Total Surface Area
Now, we can find the total surface area:
![]()
Thus, the total surface area of the hollow cylinder is approximately:
![]()
4. Applications of Hollow Cylinders
Understanding the area of hollow cylinders has practical applications in various fields:
4.1. Engineering and Manufacturing
In engineering, hollow cylinders are commonly used in the design of pipes, tubes, and structural components. Calculating the surface area is essential for determining the amount of material required for manufacturing and for assessing the structural integrity of cylindrical components.
- Illustrative Explanation: When designing a pipe, engineers need to know the surface area to calculate the amount of coating or insulation required to protect the pipe from environmental factors.
4.2. Fluid Dynamics
In fluid dynamics, hollow cylinders are often used to model pipes through which fluids flow. Understanding the surface area helps in calculating the frictional losses and flow rates within the pipe.
- Illustrative Explanation: When analyzing the flow of water through a hollow pipe, engineers can use the surface area to determine how much energy is lost due to friction against the pipe walls.
4.3. Architecture
In architecture, hollow cylinders can be used in the design of columns and structural supports. Knowing the surface area is important for assessing the load-bearing capacity and stability of these structures.
- Illustrative Explanation: When designing a column, architects must consider the surface area to ensure that the column can support the weight of the structure above it.
4.4. Storage Tanks
Hollow cylinders are also used in the design of storage tanks for liquids and gases. Calculating the surface area is crucial for determining the amount of material needed for construction and for assessing the tank’s capacity.
- Illustrative Explanation: When constructing a water storage tank, engineers need to calculate the surface area to ensure that the tank can hold the desired volume of water while maintaining structural integrity.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the area of a hollow cylinder is a fundamental concept in geometry with practical applications across various fields, including engineering, fluid dynamics, architecture, and manufacturing. By understanding the components of a hollow cylinder and the formulas for calculating its lateral surface area, area of the circular bases, and total surface area, one can effectively analyze and design cylindrical structures. The knowledge of hollow cylinders and their properties is essential for solving real-world problems and making informed decisions in engineering and design. As we continue to explore the vast landscape of geometry and its applications, the understanding of hollow cylinders will remain a key component of our mathematical toolkit.