The pentagon, a five-sided polygon, is a fundamental shape in geometry that appears in various contexts, from architecture to nature. Understanding how to calculate the area of a pentagon is essential for students, architects, engineers, and anyone involved in design and construction. This article will explore the properties of pentagons, the formulas used to calculate their area, and illustrative examples to enhance comprehension.
What is a Pentagon?
Definition
A pentagon is a polygon with five sides and five angles. The term “pentagon” is derived from the Greek words “pente,” meaning five, and “gonia,” meaning angle. Pentagons can be classified into two main categories: regular and irregular.
1. Regular Pentagon: A regular pentagon has all sides of equal length and all interior angles equal to ![]() . The symmetry and uniformity of a regular pentagon make it aesthetically pleasing and often used in design.
. The symmetry and uniformity of a regular pentagon make it aesthetically pleasing and often used in design.
2. Irregular Pentagon: An irregular pentagon has sides and angles of different lengths and measures. The lack of uniformity in an irregular pentagon can make it more complex to analyze.
- Illustrative Explanation: Imagine a regular pentagon as a perfectly shaped starfish with equal arms, while an irregular pentagon resembles a more asymmetrical starfish with uneven arms. Both are pentagons, but their properties differ significantly.
Properties of a Pentagon
1. Number of Sides: A pentagon has five sides.
2. Number of Angles: A pentagon has five interior angles.
3. Sum of Interior Angles: The sum of the interior angles of a pentagon can be calculated using the formula:
![]()
where ![]() is the number of sides. For a pentagon:
is the number of sides. For a pentagon:
![]()
4. Exterior Angles: The sum of the exterior angles of any polygon, including a pentagon, is always ![]() .
.
- Illustrative Explanation: Picture a pentagon drawn on a piece of paper. If you were to measure each of the five angles inside, you would find that they add up to
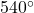 , just like how the angles in a triangle add up to
, just like how the angles in a triangle add up to 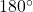 .
.
Calculating the Area of a Pentagon
The area of a pentagon can be calculated using different methods, depending on whether it is regular or irregular. Below, we will explore the formulas for both types.
1. Area of a Regular Pentagon
The area ![]() of a regular pentagon can be calculated using the following formula:
of a regular pentagon can be calculated using the following formula:
![]()
Where:
 = length of a side of the pentagon.
= length of a side of the pentagon.
Derivation of the Formula
The formula for the area of a regular pentagon can be derived using trigonometry and the properties of triangles. A regular pentagon can be divided into five identical isosceles triangles, each with a vertex angle of ![]() (since
(since ![]() ).
).
1. Calculate the Area of One Triangle: The area of one triangle can be calculated using the formula:
![]()
In this case, the base is the side length ![]() , and the height can be found using trigonometric functions.
, and the height can be found using trigonometric functions.
2. Total Area: Multiply the area of one triangle by five to get the total area of the pentagon.
- Illustrative Explanation: Imagine cutting a regular pentagon into five equal triangular slices, like a pizza. Each slice has the same area, and when you add them together, you get the total area of the pentagon.
Example Calculation
Suppose we have a regular pentagon with a side length of ![]() units. To find the area:
units. To find the area:
1. Substitute ![]() into the area formula:
into the area formula:
![]()
2. Calculate:
![]()
![]()
Thus, the area of the regular pentagon is approximately ![]() square units.
square units.
2. Area of an Irregular Pentagon
Calculating the area of an irregular pentagon can be more complex, as it does not have a uniform shape. However, one common method is to divide the irregular pentagon into simpler shapes (such as triangles and rectangles), calculate the area of each shape, and then sum them up.
Using the Shoelace Theorem
Another method to calculate the area of an irregular pentagon is to use the Shoelace Theorem, which is particularly useful when the coordinates of the vertices are known.
1. Coordinates of Vertices: Let the vertices of the pentagon be ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() , and
, and ![]() .
.
2. Shoelace Formula:
![]()
- Illustrative Explanation: Imagine plotting the vertices of an irregular pentagon on a graph. By connecting the dots and applying the Shoelace Theorem, you can find the area enclosed by the shape, similar to how a gardener measures the area of a flower bed by outlining its edges.
Example Calculation Using the Shoelace Theorem
Consider an irregular pentagon with vertices at the following coordinates:
1. Apply the Shoelace Formula:
![]()
2. Calculate:
![]()
![]()
Thus, the area of the irregular pentagon is ![]() square units.
square units.
Conclusion
The area of a pentagon, whether regular or irregular, can be calculated using various methods, each suited to the specific properties of the shape. Understanding the formulas and techniques for calculating the area of pentagons is essential for students and professionals in fields such as architecture, engineering, and design. By exploring the properties, calculations, and applications of pentagons, we gain a deeper appreciation for this fundamental geometric shape and its significance in both mathematics and the real world. Whether you are measuring the area of a garden, designing a building, or studying geometry, the principles of pentagons will continue to play a vital role in your endeavors.