Congruence of triangles is a fundamental concept in geometry that deals with the relationship between triangles that are identical in shape and size. Understanding triangle congruence is essential for students, educators, and professionals in fields such as architecture, engineering, and design. This article will explore the definitions, criteria, properties, and applications of triangle congruence, providing detailed explanations and illustrative examples to enhance comprehension.
What is Congruence?
Definition of Congruence
In geometry, two figures are said to be congruent if they have the same shape and size. This means that one figure can be transformed into the other through a series of rigid motions, such as translation (sliding), rotation (turning), or reflection (flipping), without altering its dimensions.
- Illustrative Explanation: Imagine two identical pieces of paper cut into the shape of a triangle. If you place one triangle on top of the other, they will perfectly overlap, demonstrating that they are congruent. This is similar to how two identical keys can open the same lock; they are congruent in function and form.
Notation for Congruence
The symbol for congruence is ![]() . If triangle
. If triangle ![]() is congruent to triangle
is congruent to triangle ![]() , we write:
, we write:
![]()
This notation indicates that the corresponding sides and angles of the two triangles are equal.
Criteria for Triangle Congruence
There are several criteria used to determine whether two triangles are congruent. These criteria are based on the relationships between their sides and angles. The most commonly used criteria are:
1. Side-Side-Side (SSS) Congruence
If three sides of one triangle are equal in length to three sides of another triangle, then the two triangles are congruent.
- Illustrative Explanation: Imagine measuring the sides of two triangles with a ruler. If triangle
 has sides
has sides 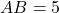 cm,
cm, 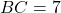 cm, and
cm, and 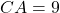 cm, and triangle
cm, and triangle 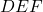 has sides
has sides 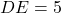 cm,
cm, 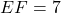 cm, and
cm, and 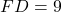 cm, then by the SSS criterion, we can conclude that
cm, then by the SSS criterion, we can conclude that 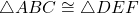 .
.
2. Side-Angle-Side (SAS) Congruence
If two sides of one triangle are equal in length to two sides of another triangle, and the angle included between those sides is equal, then the two triangles are congruent.
- Illustrative Explanation: Consider two triangles where
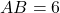 cm,
cm, 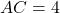 cm, and the angle
cm, and the angle 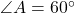 in triangle
in triangle  . If triangle
. If triangle 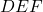 has
has 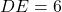 cm,
cm, 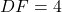 cm, and
cm, and 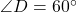 , then by the SAS criterion, we can conclude that
, then by the SAS criterion, we can conclude that 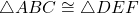 .
.
3. Angle-Side-Angle (ASA) Congruence
If two angles of one triangle are equal to two angles of another triangle, and the side included between those angles is equal, then the two triangles are congruent.
- Illustrative Explanation: Imagine triangle
 where
where 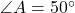 ,
, 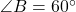 , and the side
, and the side 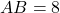 cm. If triangle
cm. If triangle 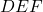 has
has 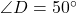 ,
, 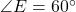 , and
, and 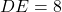 cm, then by the ASA criterion, we can conclude that
cm, then by the ASA criterion, we can conclude that 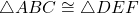 .
.
4. Angle-Angle-Side (AAS) Congruence
If two angles of one triangle are equal to two angles of another triangle, and a side not included between those angles is equal, then the two triangles are congruent.
- Illustrative Explanation: Consider triangle
 where
where 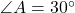 ,
, 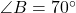 , and the side
, and the side 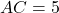 cm. If triangle
cm. If triangle 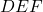 has
has 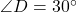 ,
, 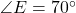 , and
, and 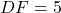 cm, then by the AAS criterion, we can conclude that
cm, then by the AAS criterion, we can conclude that 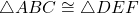 .
.
5. Hypotenuse-Leg (HL) Congruence (Right Triangles Only)
In right triangles, if the hypotenuse and one leg of one triangle are equal to the hypotenuse and one leg of another triangle, then the two triangles are congruent.
- Illustrative Explanation: Imagine two right triangles where the hypotenuse of triangle
 is
is 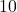 cm and one leg
cm and one leg 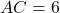 cm. If triangle
cm. If triangle 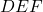 has a hypotenuse of
has a hypotenuse of 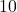 cm and one leg
cm and one leg 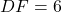 cm, then by the HL criterion, we can conclude that
cm, then by the HL criterion, we can conclude that 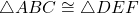 .
.
Properties of Congruent Triangles
Congruent triangles have several important properties:
1. Corresponding Sides are Equal: If two triangles are congruent, then their corresponding sides are equal in length.
2. Corresponding Angles are Equal: If two triangles are congruent, then their corresponding angles are equal in measure.
3. Rigid Motions: Congruent triangles can be transformed into one another through rigid motions (translations, rotations, and reflections) without changing their size or shape.
- Illustrative Explanation: If you have two congruent triangles, you can slide one triangle over the other, rotate it, or flip it, and they will still match perfectly, just like two identical puzzle pieces.
Applications of Triangle Congruence
Triangle congruence has numerous applications in various fields, including:
1. Construction and Engineering
In construction and engineering, congruent triangles are used to ensure structural integrity. For example, trusses in bridges and roofs often rely on congruent triangles to distribute weight evenly.
- Illustrative Explanation: Imagine a bridge made of triangular trusses. Each triangle must be congruent to ensure that the weight is evenly distributed, just like how a well-balanced seesaw works.
2. Computer Graphics
In computer graphics, congruent triangles are used in rendering images and animations. By using congruent triangles, designers can create realistic shapes and objects.
- Illustrative Explanation: Think of a video game character made up of many small triangles. Each triangle must be congruent to maintain the character’s shape as it moves, similar to how a puppet maintains its form when manipulated.
3. Geometric Proofs
In geometry, congruence is often used in proofs to establish relationships between different shapes. Proving that triangles are congruent can help deduce properties of other geometric figures.
- Illustrative Explanation: Imagine a detective solving a mystery. By proving that two triangles are congruent, the detective can uncover hidden relationships, just like piecing together clues to solve a case.
4. Art and Design
Artists and designers often use congruent triangles to create visually appealing patterns and structures. Understanding triangle congruence allows them to maintain symmetry and balance in their work.
- Illustrative Explanation: Consider a quilt made of triangular patches. Each patch must be congruent to create a harmonious design, similar to how a musician ensures that each note fits perfectly within a melody.
Conclusion
The congruence of triangles is a fundamental concept in geometry that provides a framework for understanding the relationships between shapes. By exploring the criteria for triangle congruence, the properties of congruent triangles, and their applications in various fields, we gain a deeper appreciation for this essential geometric principle. Whether in construction, computer graphics, geometric proofs, or art, the concept of triangle congruence plays a vital role in ensuring accuracy, symmetry, and beauty in our world. As we continue to study and apply these principles, we unlock new possibilities in mathematics and beyond, enhancing our understanding of the shapes that surround us.