The cube is one of the most fundamental three-dimensional geometric shapes in mathematics and geometry. It is a special type of polyhedron that has unique properties and applications across various fields, including mathematics, architecture, art, and science. This article will provide a detailed exploration of the cube, including its definition, properties, formulas for surface area and volume, methods of construction, and illustrative examples to enhance understanding.
Definition of a Cube
A cube is a three-dimensional geometric figure with six equal square faces, twelve equal edges, and eight vertices. It is also known as a regular hexahedron and is one of the five Platonic solids. Each face of a cube is a square, and all angles between the faces are right angles (90 degrees). The cube is a special case of a rectangular prism where all sides are of equal length.
Illustrative Example: Consider a cube with a side length of ![]() . Each face of the cube is a square with an area of
. Each face of the cube is a square with an area of ![]() , and the cube has a total of six faces.
, and the cube has a total of six faces.
Properties of a Cube
1. Faces: A cube has six faces, all of which are squares. Each face is congruent to the others.
2. Edges: A cube has twelve edges. Each edge is of equal length ![]() .
.
3. Vertices: A cube has eight vertices (corners). Each vertex is the point where three edges meet.
4. Diagonals: A cube has two types of diagonals:
– Face Diagonals: Diagonals that lie on the faces of the cube. Each face diagonal can be calculated using the formula ![]() .
.
– Space Diagonals: Diagonals that pass through the interior of the cube, connecting opposite vertices. The length of a space diagonal can be calculated using the formula ![]() .
.
5. Symmetry: A cube has a high degree of symmetry. It has 24 rotational symmetries and 9 reflectional symmetries, making it a highly symmetrical shape.
Formulas Related to a Cube
Understanding the formulas related to a cube is essential for calculating its surface area and volume, which are fundamental in various applications.
1. Surface Area: The surface area ![]() of a cube can be calculated using the formula:
of a cube can be calculated using the formula:
![]()
Where ![]() is the length of one side of the cube. This formula arises because there are six square faces, each with an area of
is the length of one side of the cube. This formula arises because there are six square faces, each with an area of ![]() .
.
Illustrative Example: For a cube with a side length of ![]() cm, the surface area is:
cm, the surface area is:
![]()
2. Volume: The volume ![]() of a cube can be calculated using the formula:
of a cube can be calculated using the formula:
![]()
Where ![]() is the length of one side of the cube. This formula represents the total space enclosed within the cube.
is the length of one side of the cube. This formula represents the total space enclosed within the cube.
Illustrative Example: For a cube with a side length of ![]() cm, the volume is:
cm, the volume is:
![]()
Visualization of a Cube
To visualize a cube, consider the following diagram:
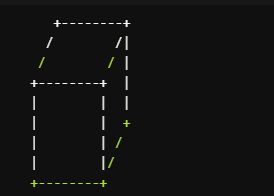
In this diagram, the cube is represented in a three-dimensional perspective. The vertices are labeled, and the edges are shown connecting the vertices. Each face of the cube is a square, and the overall shape is symmetrical.
Construction of a Cube
Constructing a cube can be done using various methods, depending on the context. Here are two common methods:
1. Geometric Construction: Using a ruler and compass, one can construct a cube by following these steps:
– Start with a square base.
– Draw vertical lines from each vertex of the square to represent the height of the cube.
– Connect the corresponding vertices of the top and bottom squares to form the edges of the cube.
2. 3D Modeling Software: In modern applications, cubes can be easily constructed using 3D modeling software. Users can define the dimensions of the cube and visualize it in a virtual environment.
Applications of a Cube
Cubes have numerous applications across various fields:
1. Mathematics: Cubes are fundamental in geometry and are used to teach concepts related to volume, surface area, and spatial reasoning.
2. Architecture: In architecture, cubes are often used in the design of buildings and structures. The cube’s symmetry and simplicity make it a popular choice for modern architectural designs.
3. Art: Artists use cubes in sculpture and design to create three-dimensional works. The cube’s geometric properties can be manipulated to create visually interesting forms.
4. Science: In science, cubes are used in crystallography to study the arrangement of atoms in crystalline solids. The cubic structure is a common form for many minerals and compounds.
5. Games and Toys: Cubes are prevalent in games and toys, such as dice and building blocks. Their uniform shape allows for easy stacking and manipulation.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the cube is a fundamental three-dimensional geometric shape characterized by its six equal square faces, twelve equal edges, and eight vertices. Understanding the properties, formulas, and applications of the cube is essential for solving various mathematical problems and has practical implications in fields such as architecture, art, and science. Through detailed explanations and illustrative examples, we can appreciate the significance of the cube in both theoretical and practical contexts. Whether constructing geometric figures or applying these principles in real-world scenarios, the cube remains a cornerstone of geometric understanding, showcasing the beauty and simplicity of three-dimensional shapes.