Cylinders are one of the fundamental shapes in geometry and are widely encountered in various fields, including mathematics, engineering, architecture, and everyday life. A cylinder is a three-dimensional geometric figure with two parallel circular bases connected by a curved surface. This article will explore the definition of a cylinder, its properties, types, formulas for calculating its volume and surface area, and practical applications, along with illustrative explanations to enhance understanding.
What is a Cylinder?
Definition of a Cylinder
A cylinder is a three-dimensional solid that consists of two parallel circular bases of equal size, connected by a curved surface. The distance between the two bases is known as the height (h) of the cylinder. The line segment connecting the centers of the two bases is called the axis of the cylinder.
Illustrative Explanation of a Cylinder
To visualize a cylinder, imagine a can of soda. The can has two circular ends (the top and bottom) and a curved surface that wraps around the sides. The height of the can is the distance from the top to the bottom, while the radius is the distance from the center of the circular base to its edge.

In this diagram, the top and bottom circles represent the bases of the cylinder, while the curved lines represent the lateral surface.
Properties of a Cylinder
Cylinders have several key properties that define their characteristics:
1. Bases: A cylinder has two bases that are congruent circles.
2. Height (h): The perpendicular distance between the two bases.
3. Radius (r): The radius of the circular base, which is the distance from the center of the base to its edge.
4. Axis: The line segment that connects the centers of the two bases.
5. Lateral Surface: The curved surface that connects the two bases.
Illustrative Example of Properties
Consider a cylinder with a radius of 3 cm and a height of 5 cm. The properties can be summarized as follows:
- Radius (r): 3 cm
- Height (h): 5 cm
- Axis: The line segment connecting the centers of the top and bottom circles.
- Bases: Two circular bases, each with a radius of 3 cm.
Types of Cylinders
Cylinders can be classified into different types based on their orientation and dimensions:
1. Right Cylinder
A right cylinder has bases that are aligned directly above one another, and the sides are perpendicular to the bases. This is the most common type of cylinder.
Illustrative Example: A soda can is a right cylinder because its sides are straight and perpendicular to the circular bases.
2. Oblique Cylinder
An oblique cylinder has bases that are not aligned directly above one another, resulting in slanted sides. The sides of an oblique cylinder are not perpendicular to the bases.
Illustrative Example: A leaning tower or a slanted can would represent an oblique cylinder.
3. Circular Cylinder
A circular cylinder is a specific type of right cylinder where the bases are circular. This is the most common type of cylinder encountered in geometry.
4. Elliptical Cylinder
An elliptical cylinder has elliptical bases instead of circular ones. The sides are still perpendicular to the bases, making it a right cylinder.
Illustrative Example: A bottle with an elliptical base is an elliptical cylinder.
Formulas for Volume and Surface Area
Volume of a Cylinder
The volume (V) of a cylinder can be calculated using the formula:
![]()
Where:
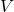 = volume of the cylinder
= volume of the cylinder = radius of the base
= radius of the base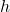 = height of the cylinder
= height of the cylinder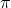 (Pi) is approximately 3.14159
(Pi) is approximately 3.14159
Illustrative Example of Volume Calculation
Let’s calculate the volume of a right cylinder with a radius of 3 cm and a height of 5 cm.
1. Identify the Variables:
– ![]()
– ![]()
2. Substitute into the Volume Formula:
![]()
Thus, the volume of the cylinder is approximately 141.37 cm³.
Surface Area of a Cylinder
The total surface area (A) of a cylinder can be calculated using the formula:
![]()
Where:
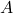 = total surface area of the cylinder
= total surface area of the cylinder = radius of the base
= radius of the base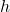 = height of the cylinder
= height of the cylinder
This formula accounts for both the lateral surface area and the area of the two circular bases.
Illustrative Example of Surface Area Calculation
Using the same cylinder with a radius of 3 cm and a height of 5 cm, we can calculate the surface area.
1. Identify the Variables:
– ![]()
– ![]()
2. Substitute into the Surface Area Formula:
![]()
Thus, the total surface area of the cylinder is approximately 150.80 cm².
Practical Applications of Cylinders
Cylinders are prevalent in various fields and have numerous practical applications:
1. Engineering and Manufacturing
Cylinders are used in the design of pipes, tanks, and pressure vessels. Understanding the volume and surface area of cylinders is crucial for ensuring structural integrity and capacity.
2. Architecture
Architects often use cylindrical shapes in building designs, such as columns and towers. The aesthetic appeal and structural properties of cylinders make them popular in architecture.
3. Everyday Objects
Many everyday objects are cylindrical in shape, including cans, bottles, and tubes. Understanding the properties of cylinders helps in packaging and storage design.
4. Physics and Mechanics
Cylinders are essential in physics, particularly in mechanics, where they are used to model rotational motion, such as in the case of wheels and gears.
5. Fluid Dynamics
In fluid dynamics, cylinders are used to study the flow of liquids and gases. The shape of a cylinder affects how fluids move around it, which is important in various engineering applications.
Conclusion
Cylinders are fundamental geometric shapes with unique properties and applications across multiple fields. Understanding the definition, properties, types, and formulas related to cylinders is essential for students, engineers, architects, and anyone involved in design and analysis. By mastering the concepts of cylinders, individuals can apply this knowledge to real-world problems, enhancing their analytical skills and understanding of three-dimensional shapes. As you continue to explore geometry and its applications, the cylinder will remain a vital shape in your mathematical toolkit.