In mathematics, functions are fundamental concepts that describe relationships between sets of elements. Understanding the terms domain, codomain, and range is essential for grasping how functions operate and how they can be analyzed. This article will provide a detailed exploration of these concepts, including definitions, illustrative explanations, and examples to enhance understanding.
1. Definition of a Function
Before delving into domain, codomain, and range, it is crucial to understand what a function is. A function ![]() is a relation that assigns each element from a set
is a relation that assigns each element from a set ![]() (called the domain) to exactly one element in a set
(called the domain) to exactly one element in a set ![]() (called the codomain). This relationship can be expressed as:
(called the codomain). This relationship can be expressed as:
![]()
Illustrative Explanation:
Consider a function that maps students to their grades. Let ![]() be the set of students, and
be the set of students, and ![]() be the set of grades. Each student is assigned a specific grade, which means that for every student in set
be the set of grades. Each student is assigned a specific grade, which means that for every student in set ![]() , there is a corresponding grade in set
, there is a corresponding grade in set ![]() .
.
2. Domain of a Function
The domain of a function is the set of all possible input values (or arguments) for which the function is defined. In other words, it is the set of all elements from the domain set ![]() that can be used as inputs to the function
that can be used as inputs to the function ![]() .
.
Mathematical Notation:
If ![]() , then the domain of
, then the domain of ![]() is denoted as:
is denoted as:
![]()
Illustrative Explanation:
Consider the function ![]() . The domain of this function consists of all non-negative real numbers because the square root of a negative number is not defined in the set of real numbers. Therefore, the domain can be expressed as:
. The domain of this function consists of all non-negative real numbers because the square root of a negative number is not defined in the set of real numbers. Therefore, the domain can be expressed as:
![]()
This means that any value ![]() in the interval from 0 to positive infinity can be used as an input for the function
in the interval from 0 to positive infinity can be used as an input for the function ![]() .
.
3. Codomain of a Function
The codomain of a function is the set of all possible output values that the function can produce. It is the set that contains the function’s values, but it may include values that are not actually produced by the function for any input from the domain.
Mathematical Notation:
If ![]() , then the codomain of
, then the codomain of ![]() is denoted as:
is denoted as:
![]()
Illustrative Explanation:
Using the same function ![]() , if we define the codomain as the set of all real numbers
, if we define the codomain as the set of all real numbers ![]() , we can express it as:
, we can express it as:
![]()
In this case, while the function only produces non-negative outputs (i.e., ![]() ), the codomain includes all real numbers, which means that there are values in the codomain that are not outputs of the function.
), the codomain includes all real numbers, which means that there are values in the codomain that are not outputs of the function.
4. Range of a Function
The range of a function is the set of all actual output values that the function produces when the inputs from the domain are applied. It is a subset of the codomain and represents the values that the function can actually take.
Mathematical Notation:
If ![]() , then the range of
, then the range of ![]() is denoted as:
is denoted as:
![]()
Illustrative Explanation:
Continuing with the function ![]() , the range consists of all the values that
, the range consists of all the values that ![]() can produce when
can produce when ![]() varies over its domain. Since the function only produces non-negative outputs, the range can be expressed as:
varies over its domain. Since the function only produces non-negative outputs, the range can be expressed as:
![]()
This indicates that the function can output any value from 0 to positive infinity, which aligns with the outputs of the function.
5. Relationship Between Domain, Codomain, and Range
To summarize the relationships between these three concepts:
- Domain: The set of all possible inputs for the function.
- Codomain: The set of all potential outputs that the function could produce, regardless of whether they are actually produced.
- Range: The actual set of outputs produced by the function when the inputs from the domain are applied.
Illustrative Example:
Let’s consider a function defined as follows:
![]()
- Domain: The domain of
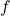 is all real numbers,
is all real numbers, 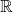 , since you can square any real number.
, since you can square any real number. - Codomain: If we define the codomain as
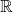 , then the codomain includes all real numbers.
, then the codomain includes all real numbers. - Range: The range of
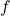 is
is 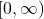 because squaring any real number will yield a non-negative result.
because squaring any real number will yield a non-negative result.
In this case, we see that the range is a subset of the codomain, which is a common scenario in functions.
6. Visual Representation
To further clarify these concepts, consider the following visual representation:
- Domain: Represented on the x-axis, showing all possible input values.
- Codomain: Represented on the y-axis, indicating all potential output values.
- Range: Highlighted within the codomain, showing the actual outputs produced by the function.
Illustrative Explanation:
Imagine a graph of the function ![]() :
:
- The x-axis (domain) extends infinitely in both directions, representing all real numbers.
- The y-axis (codomain) also extends infinitely, but the actual points plotted (the range) will only be in the non-negative region, starting from 0 and going up to infinity.
7. Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the concepts of domain, codomain, and range is essential for analyzing functions in mathematics. The domain represents all possible inputs, the codomain encompasses all potential outputs, and the range consists of the actual outputs produced by the function. By grasping these concepts, one can better understand how functions operate and how to manipulate them in various mathematical contexts. Through illustrative explanations and examples, we can appreciate the significance of these terms in mathematical reasoning and their practical applications in real-world scenarios. As we continue to explore the world of mathematics, the clarity of these concepts will enhance our ability to analyze and work with functions effectively, leading to deeper insights and understanding in various fields of study.